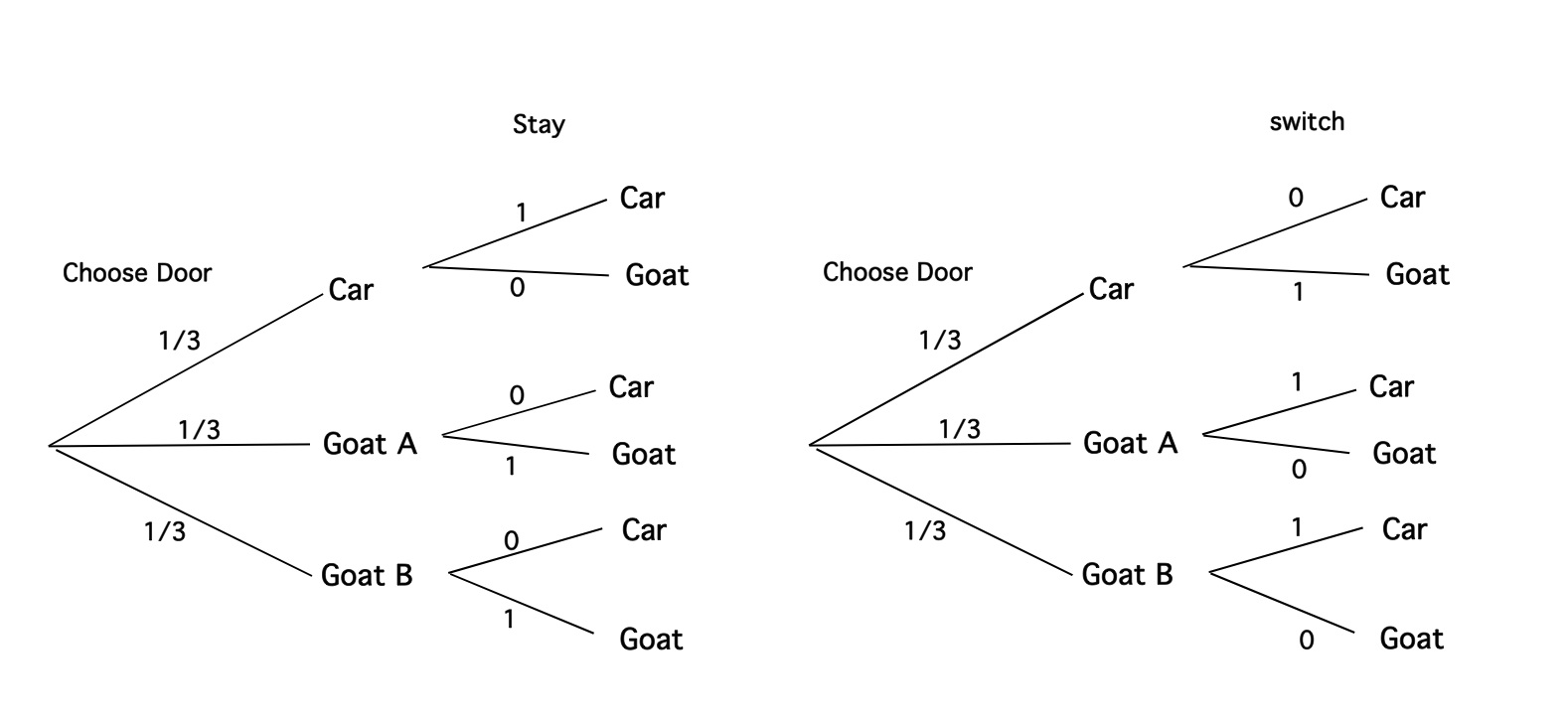
Monty Hall Problem Math Proof
P 3 1 Suppose that the contestant chooses door number 1. A box containing two gold coins a box with two silver coins and a box with one of each coin.
2 Ways To Look At The Monty Hall Problem By Shen Huang Medium
You can implement other Monty Hall behaviors by changing how you assign the four probabilities.

Monty hall problem math proof. Behind each door there is either a car or a goat. First off Bayes Theorem states. Try playing the game 50 times using a pick and hold strategy.
. And formal mathematical proofs. The Math Behind the Fact.
The Monty Hall Problem or Monty Hall Paradox as it is known is named after the host of the popular game show Lets Make a Deal in the 1960s and 70s who presented contestants with exactly this scenario. Now the gain when declining to switch is given by how many cases have the car behind door A. Minecraft shortscheck out my so.
The novel contains some memorable passages outlining the Monty Hall Problem in the heros voice. There are three inverted cups one of which hides a valuable diamond. In this paradox there are three boxes.
Suppose youre on a game show and youre given the choice. In other words the probability that the car is behind Door B and the probability that the car is behind Door C must necessarily add up to 23. Door.
Just pick door 1 or 2 or 3 and keep clicking. It was later published in Marilyn Vos Savants column in Sunday. You pick one of three doors at random.
We then provide a mathematical explanation that fits the experimental results. Noting that 0. A contestant chooses one of the three cups at random Move One.
Youll see it settle around 13. Now the gamemaster opens a different door with a goat and asks you if you want to switch. The Monty Hall problem is a famous seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes theorem.
If there is a 13 chance that Door A has the car behind it then there is a 23 chance that the car is behind either Door B or Door C. In this video i go over the monty hal problemmake sure to subscribe for more. Proof of the Monty Hall Problem.
Since the sample space is reducedd from the total space to A and the probability that B will occur given that A has occured is. Conditional ProbabilityThe Monty Hall Problem Sometimes we already know the ocurrence of an event A then the probability of a relevent event B given A is different from PB without any information on A. The answer is YES you should switch because the probability that you will find the car by doing so.
If your in front of a door with a goat then you would win if. Look at your percent win rate. 2 1 3.
Monty Hall who knows where the diamond is must eliminate one of the empty unchosen cups leaving only two cups on the table Move Two. Hey its me gabe gabesweats from tiktok. After choosing a box at random and withdrawing.
RULES of the GAME. 1 The probability that the prize is behind door 1 2 or 3 is 3 P. I would state my proof as follows.
At this point the probability of success ie choosing the diamond is 13. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldnt. In this paper we define the Monty Hall problem and use a computer simulation to shed light on it.
The probability that you hit a door with a goat is 2 3. Task 5 in the second class activity requiring a math proof in prose was inspired by this A version of the Monty Hall problem was a regular feature of the American television game show Lets Make a Deal named after its host Monty Hall. In the problem you are on a game show being asked to choose between three doors.
The Monty Hall problem is based on apparent paradox that is commonly misun- derstood even by mathematicians. So they happen to get the right answer. The final way to solve the Monty Hall Problem that I will discuss Bayes Theorem is the most mathematically involved proof of the solution.
Another pass at the Monty Hall Problem - see the last video and a new express explanation at. Sumcar A n. Now reset and play it 20 times using a pick and switch approach.
The Monty Hall problem first graced the world of mathematics in 1990 with a letter sent to Marilyn von Savant an American magazine columnist who at the time was listed in the Guinness Book of World Records as having the highest recorded IQ of anyone alive. One of the early probability puzzles related to the Monty Hall Problem dates back to Joseph Bertrands Box Paradox posed in 1889. HttpbitlyMontyHallProbMore links stuff in full descrip.

Conditional Probability Monty Hall Problem Youtube
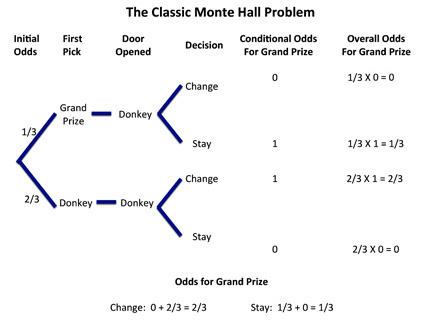
The Monty Hall Problem Revisited Again

Monty Hall Problem Explained Python Code For Simulating Monty Hall Problem

Could The Monty Hall Problem Be Applied To Multiple Choice Tests Mathematics Stack Exchange

1 The Monty Hall Problem Odds Ends
Why Is The Chance Not 50 50 In The Monty Hall Problem Quora
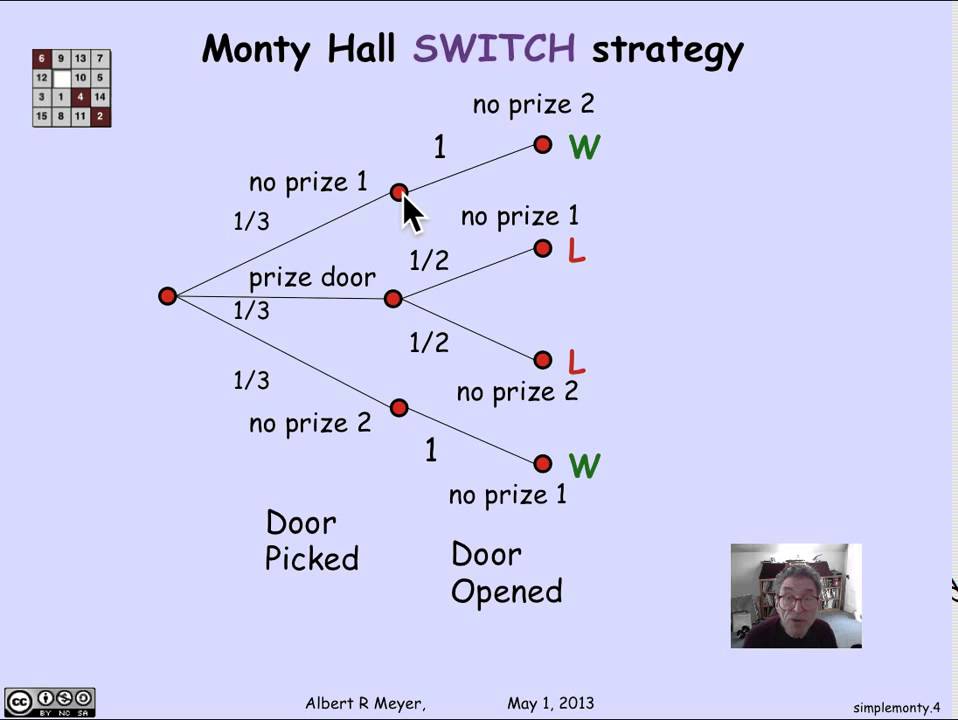
4 1 3 Simplified Monty Hall Tree Video Youtube
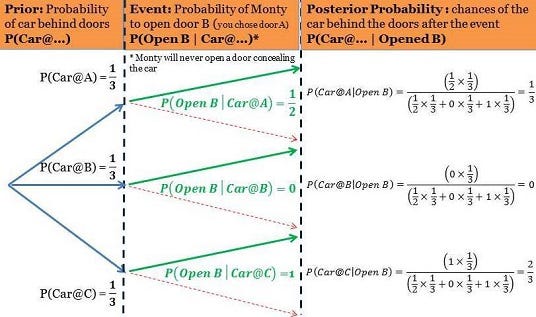
Applying Bayes Theorem Simulating The Monty Hall Problem With Python By Nickdoesdata Medium
4 The Monty Hall Problem Solution And Implications Game Theory

Bayes Theorem Monty Hall Problem You Canalytics

The Monty Hall Problem Or When The Obvious Isn T
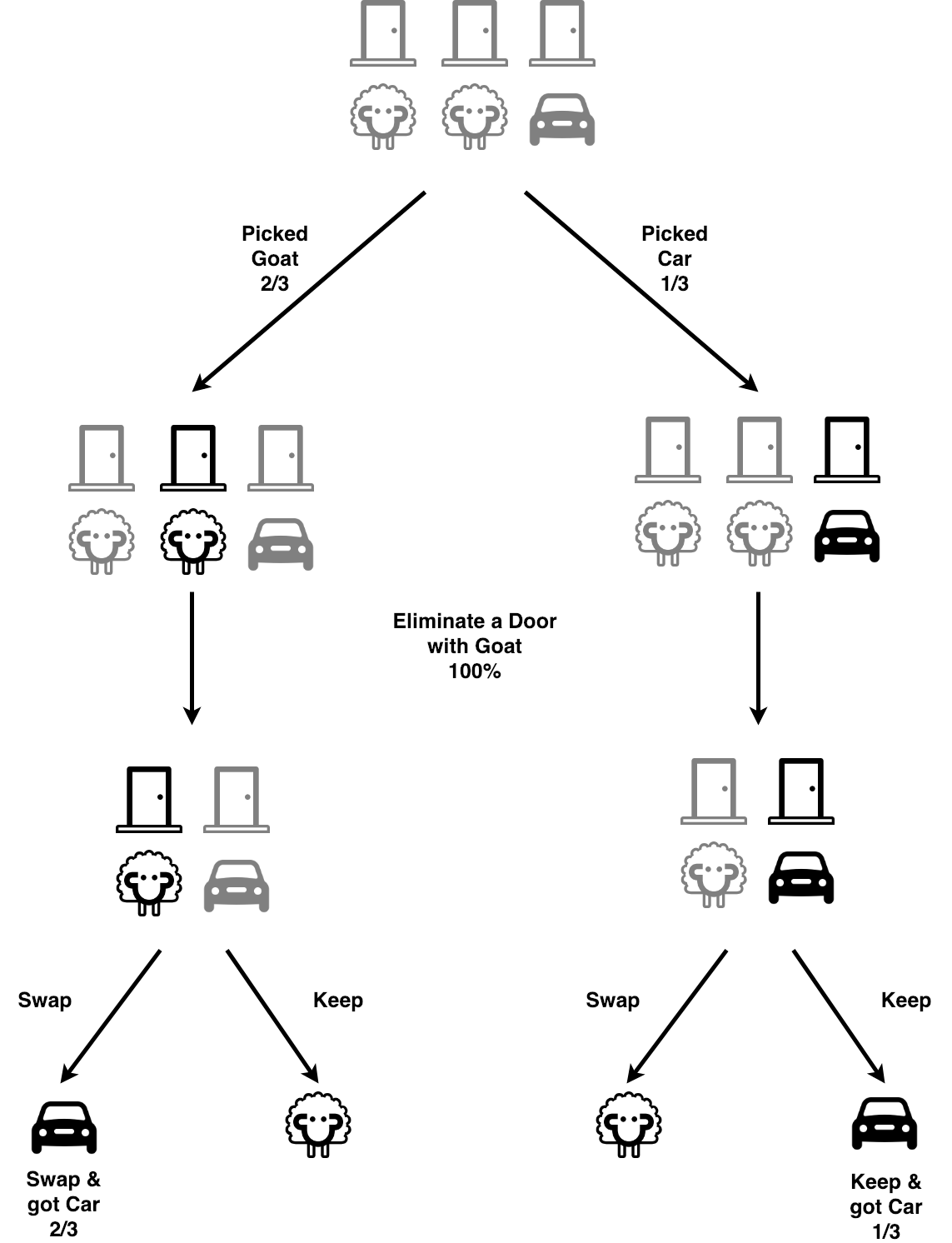
2 Ways To Look At The Monty Hall Problem By Shen Huang Medium
Graphical Proof Of The Monty Hall Problem

Monty Hall Three Door Game Mathematics Stack Exchange